Your Destination for PRP Joint Solutions
We understand.
Are you tired of living with joint pain that limits your mobility and quality of life? PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Joint Solutions that can help rejuvenate your joints and bring back the comfort and freedom you deserve.
Why wait?
At Blue Med Center and Spa, we understand the impact joint pain can have on your daily activities. Our PRP Joint Solutions provide a non-surgical and natural approach to healing and rejuvenating your joints. Platelet-Rich Plasma therapy utilizes your body’s own healing mechanisms to promote tissue repair and regeneration, effectively targeting the root cause of your joint discomfort.
Why Chose Blue Med Center?
expertise
Our team consists of experienced medical professionals who specialize in PRP therapies. With a deep understanding of the latest advancements in regenerative medicine, our experts will guide you through a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique needs.
customized Care
We recognize that every individual’s body responds differently. Our treatments are tailored to your unique physiology, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
innovation
We utilize advanced medical technologies that are both safe and effective. Our treatments are backed by science and designed to deliver noticeable results.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Joint Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a medical treatment that involves the injection of a concentrated solution of a patient’s own platelets and growth factors into an injured or degenerated joint. PRP therapy is often used to promote healing and reduce pain in musculoskeletal conditions.
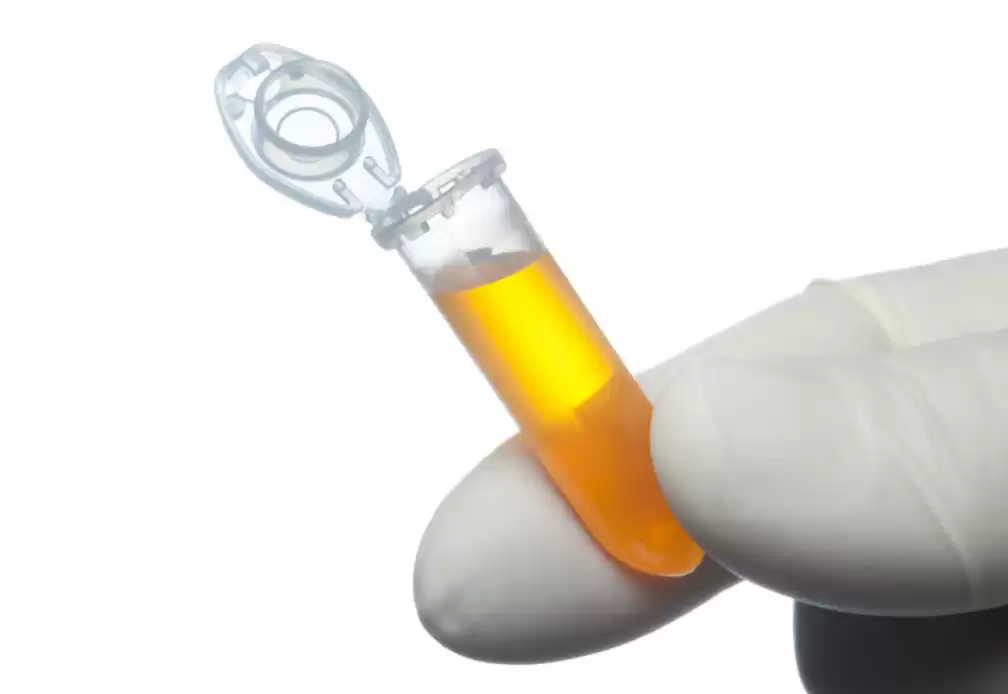
Benefits of PRP Joint Therapy
Pain Relief
PRP therapy can help reduce pain in the affected joint, which is especially beneficial for individuals with conditions like osteoarthritis or tendinopathy.
Improved Function
By promoting tissue repair and regeneration, PRP therapy can enhance joint function, leading to improved mobility and range of motion.
Non-Surgical Approach
PRP therapy is a minimally invasive and non-surgical treatment option, making it an attractive choice for individuals who want to avoid surgery or are not good candidates for it.
Natural Healing
PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood, which reduces the risk of allergic reactions or rejection. This makes it a safe and natural option for joint therapy.
Short Recovery Time
Compared to surgical interventions, PRP therapy typically involves a shorter recovery period, allowing patients to return to their regular activities sooner.
Low Risk of Side Effects
Since PRP is made from the patient’s own blood, the risk of adverse reactions or side effects is minimal.
Improved Function
By promoting tissue repair and regeneration, PRP therapy can enhance joint function, leading to improved mobility and range of motion.
Promotes Tissue Healing
PRP contains growth factors that can stimulate tissue repair and regeneration, which is beneficial for healing damaged cartilage, tendons, and ligaments.
Long-Lasting Effects
Some individuals experience sustained pain relief and improved joint function for an extended period after PRP therapy, potentially delaying the need for further treatments.
What you can expect...
Consultation & Evaluation
Your journey begins with a comprehensive consultation. Our medical experts will assess your condition, discuss your medical history, and answer any questions you may have about PRP therapy.
Personalized Treatment
Based on your consultation, we will create a personalized PRP treatment plan. This plan may involve injections directly into the affected joint, delivering a concentrated dose of growth factors and healing properties.
The PRP Procedure
Your medical provider will first draw about 30 ml of blood and use a centrifuged to separate the platelets from other blood components. The platelet rich portion of the blood is extracted for reinjection. The process of preparing your PRP takes about 20 minutes. Once the area being treated has been properly sterilized, a local anesthetic agent is used and the PRP is injected into the affected area.
Comfort and Care
Our priority is your comfort. Our spa-like environment is designed to help you relax during your treatment sessions. We make managing any discomfort a priority.
Results and Recovery
Following the procedure, you can resume your daily routine activities but should avoid strenuous activities such as heavy exercise or lifting. Any discomfort following treatment, is generally mild in nature and should subside within a few days. Cold compresses and over-the-counter pain medications are usually sufficient to keep you comfortable. Anti-inflammatory medications are to be avoided for up to 48 hours after the injection, as they can affect the platelet function.

Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy for Shoulder Pain
- Arthritis
- Bicipital Tendonitis
- Instability
- Labrum Tears
- Rotator Cuff Impingement Syndrome or Bursitis
- Rotator Cuff Tendonitis or Tear
Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy for Knee Pain
- Arthritis
- Meniscus Tears
- Partially Torn or Strained Major Ligaments of the Knee (ACL/ LCL/ MCL)
- Patellar Femoral Syndrome
- Patellar Instability
- Patellar Tendonitis
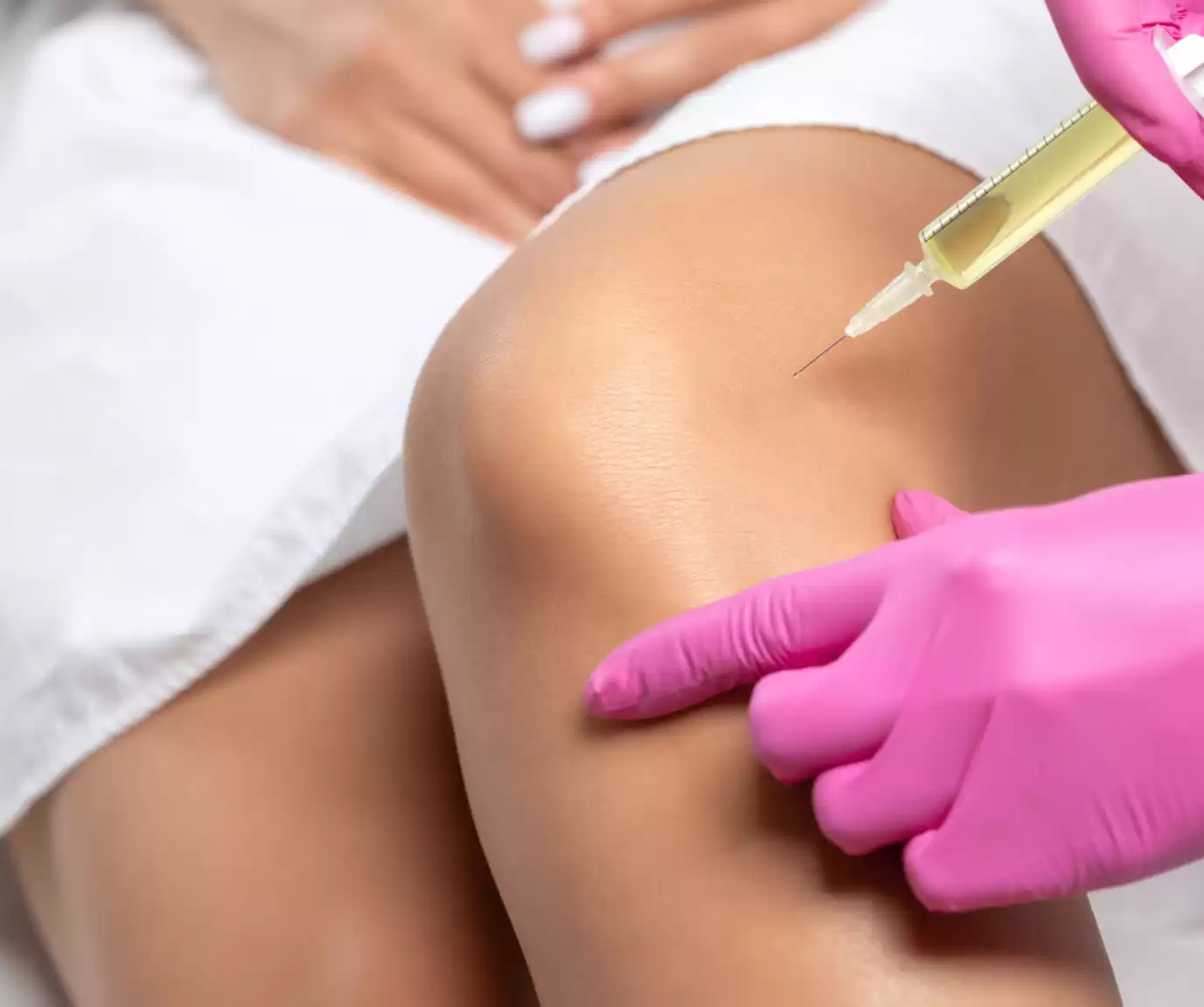

Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy for Elbow Pain
- Arthritis
- Medial and Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow)
Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy for Ankle and Foot Pain
- Achilles Tendonitis
- Arthritis
- Chronic lower back pain
- Knee osteoarthritis
- Morton’s neuroma
- Other Foot or Ankle Tendinitis
- Peroneal Tendonitis
- Plantar fasciitis
- Recurrent Ankle Sprains
Don’t let joint pain hold you back any longer.
Contact us today to schedule your consultation and discover how our PRP Joint Solutions can bring back the joy of pain-free movement. Regain your life – one step at a time!
Research Studies
National Library of Medicine
The temporal effect of platelet-rich plasma on pain and physical function in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis:
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Click to Read
National Library of Medicine
MRI Changes After Platelet Rich Plasma Injection in Knee Osteoarthritis (Randomized Clinical Trial).
Click to Read
National Library of Medicine
Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial.
Click to Read
National Library of Medicine
Comparison of the Clinical Effectiveness of Single Versus Multiple Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Click to Read

